Investors Miss Out When Tax Deals Are Concealed
Companies that get non-income tax breaks from state and local governments have higher sales and stock returns
Based on the research of Brady Williams
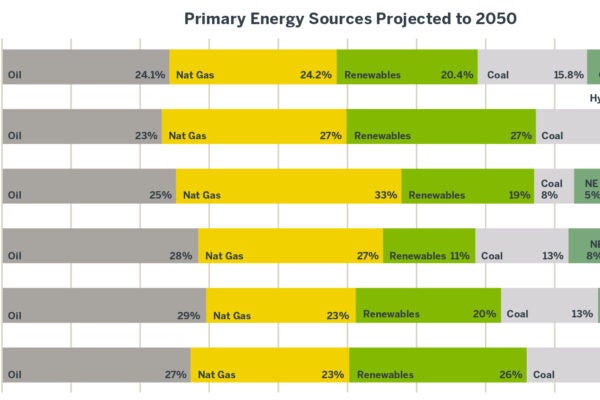
In 2022, U.S. corporations reaped more than $19 billion in non-income tax megadeals: state and local tax breaks worth $50 million or more. That’s according to Good Jobs First, a nonprofit that tracks tax subsidies for corporate facilities.
Investors could benefit if they had timely information about such tax deals, says Brady Williams, associate professor of accounting at Texas McCombs. In new research, he finds that companies that get them have higher future stock returns.
Unfortunately, investors don’t get such information. Accounting rules don’t require companies to disclose the deals in financial statements. By the time they make it into GJF’s database, they’re often months or years old.
“What we show in this paper couldn’t be a viable real-time trading strategy,” Williams says. “This paper highlights the inadequacy of the information environment around non-income taxes.”
With Michael Drake of Brigham Young University, Ryan Hess of Oklahoma State University, and Jaron Wilde of the University of Iowa, Williams analyzed tax incentive deals from GJF’s database. Covering 1,031 state and local governments from 2003 to 2016, the researchers found:
· For companies that got tax breaks, sales the following year were 9.6% higher than for comparable companies that did not.
· Tax breaks boosted their stock returns 4.1%, compared with companies that did not get them.
It’s not clear whether the tax breaks helped generate the higher sales and returns, Williams cautions. He notes that governments tend to award them to companies whose prospects are already bright.
“A major company comes to a city or county and says, ‘We have financing secured, we think we have the demand, and we’re willing to back that up with hundreds of millions of dollars of investment in your jurisdiction,’” he says. “That’s essentially a signal of private information that the market might not be privy to at the moment.”
Should companies be required to disclose non-income tax deals in their financials? Not necessarily, says Williams. Making such deals public too soon might discourage governments from offering them and remove one lever they can use to stimulate the local economy.
What’s clear is the impact on investors, he says. “The results suggest that they could make more informed trading decisions if they had access to this information.”
“The Relevance of Non-Income Tax Relief” is published in Contemporary Accounting Research.
Story by Steve Brooks
About this Post
Share: